Tutorial: Haskell
Haskell is a functional programming language. Functions and programs are like mathematical equations. It is really fun to play with.
Contents:
The Basics
-
Basics
-
Algebraic Data Types
-
Maybe Data Type
Abstract Data Types:
-
Linked List
-
Queue
-
Arithmetic Tree
-
Graphs
-
Heaps
The Basics
To Install:
For Linux, it can be installed with apt
sudo apt-get install haskell-platform
GHCI:
GHCI is an interactive environment for the Glasglow Haskell Compiler. It is used to interactively evaluate expressions, and compile and run haskell files.
//In terminal:
~$ ghci
//To quit:
:quit
//To get type of variable:
:t [variable]
//To load from file:
:l [filename]
Comments:
-- I am a single line comment
{--I am a multiline comment --}
Types:
-- Ints
a=5
-- Floats
a=5.23
-- Chars
a='a'
-- Strings:
a="abcd"
-- or
a=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
-- Lists, must all have the same data type
-- Ex: An integer list, type: [Int]
a=[1,2,3,4]
-- Tuples, can have different types
-- Ex:
a=(1,2,'a', [1,2,3])
List Operations:
Examples of list operations performed on list a=[1,2,3,4]
-- A list of ints
a=[1,2,3,4]
-- Get the first element:
head a
1
-- Get every element but the first:
tail a
[2,3,4]
-- Get the last element:
last a
4
-- Get every element but the last:
init a
[1,2,3]
-- Returns true if list is empty, false otherwise
null a
False
-- reverse the order of the list
reverse a
[4,3,2,1]
-- get length of list
length a
4
-- get first n elements of the list
take 2 a
[1,2]
-- drop first n elements of the list
drop 2 a
[3,4]
-- get largest element in a list
maximum a
4
-- get smallest element in a list
minimum a
1
-- get the sum of the elements in the list
sum a
10
-- get the product of the elements in the list
product a
24
-- check if element is a list
elem 5 a
False
-- concat 2 lists:
a ++ [5,6]
[1,2,3,4,5,6]
-- Add an element to a list:
5 : a
[5,1,2,3,4]
-- OR:
[5] ++ a
[5,1,2,3,4]
List Comprehensions:
Is the process of generating a list using a mathematical expression, always in the format: [operation | range, condition]
-- Example: double every element in a list
a = [1,2,3,4]
[x*2 |x <- a]
[2,4,6,8]
-- double only even numbers:
[x*2 | x <- a, (even x)]
[4,8]
-- double even numbers, triple odd numbers:
[if even x then x*2 else x*3 | x <- a]
[3,4,9,8]
Sequence/Range Operator:
Gets all the values within a certain range, can be used with chars as well. Must be ascending order
-- Ex:
[1..10]
--OUT:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
['a'..'g']
--OUT:
"abcdefg"
[10..1]
--OUT:
[]
Functions:
Functions consist of 2 parts: declaration, and definition. A function declaration has the format: myFunc :: arg1 -> arg2 -> outVal, and a function definition defines the operation to be performed by the function.
-- Ex: Sum of 2 ints
mySum:: Int -> Int -> Int
mySum x y = x+y
--To call the function:
(mySum 2 4)
-- OUT:
6
Pattern Matching:
Pattern matching allows functions to execute differently depending on their arguments
-- Ex: Recursive function calculating factorial
myFact:: Int -> Int
myFact 0 = 1
myFact n = n * (fact (n-1))
--To call the function:
myFact 4
-- OUT:
24
Guards:
Match 1 or more expressions, use guards to test some property of an expression, guards are seperated by |, they allow for different operations to be performed depending on the input params.
-- Ex: Recursive function calculating factorial
myFact :: Int -> Int
myFact n | n == 0 = 1
| otherwise = (fact (n-1))
--To call the function:
myFact 4
-- OUT:
24
Where clause:
Used to break complex expressions into smaller parts
-- Ex: Recursive function calculating nth term of the fibonacci sequence
myFib:: Int -> Int
myFib 0 = 0
myFib 1 = 1
myFib n = m where m = (myFib (n-1)) + (myFib (n-2))
--To call the function:
myFib 5
-- OUT:
5
Lambda Expressions:
anonymous function, can only be used once (ie. cannot be called), is denoted by \
-- Ex: Increase by one
((\x-> x + 1) 4)
--OUT:
5
Higher Order Functions:
Accumulation (Folding) - apply a binary operator between the elements of a list,
Format: fold (operator) (accumulator) list,
foldl - accumulator left side arguement (ex. accumulator - myList[i]),
foldr - accumulator right side arguement (ex. myList[i] - accumulator)
-- Ex:
foldl (+) 0 [1,2,3]
6
foldl (-) 12 [1,2,3]
6
foldr (-) 12 [1,2,3]
-10
Transformation (Mapping) - call a function on every element in a list
Format: map (operator) list
map (+2) [1,2,3]
[3,4,5]
map (*2) [1,2,3]
[2,4,6]
Selection(Filtering) - Test a predicate for every element of a list
Format: filter (boolean condition) myList
filter (even) [1,2,3]
[2]
filter (<10) [8, 9, 10]
[8,9]
filter (=='a') ['a','a', 'b', 'c']
"aa"
Algebraic Data Types:
Algebraic Data Types are user defined data types, sort of like objects. They can have attributes, and can be used in operations.
-- Ex:
data Food = Cake | Spinach | Apple
myFoods :: Food -> [Char]
myFoods Cake = "Yum!"
myFoods Spinach = "Yuck"
myFoods Apple = "Nice Healthy Choice"
-- Run
myFoods Apple
--OUT:
"Nice Healthy choice"
Example: Truth Table:
-- A) Define enumerated data type
data LogicDataType = Trwue
| Fawlse
| Unkwown
deriving Show
-- Logical NOT
ternaryNOT :: LogicDataType -> LogicDataType
ternaryNOT Trwue = Fawlse
ternaryNOT Fawlse = Trwue
ternaryNOT a = a
-- Logical AND
ternaryAND :: LogicDataType -> LogicDataType -> LogicDataType
ternaryAND Trwue Trwue = Trwue
ternaryAND Fawlse a = Fawlse
ternaryAND a Fawlse = Fawlse
ternaryAND a b = Unkwown
-- Logical OR
ternaryOR :: LogicDataType -> LogicDataType -> LogicDataType
ternaryOR Fawlse Fawlse = Fawlse
ternaryOR Trwue a = Trwue
ternaryOR b Trwue = Trwue
ternaryOR a b= Unkwown
-- Run
ternaryOR Trwue Fawlse
-- OUT:
Trwue
Maybe Data Type:
An enumerated type that allows you to work with a value that might not exist
Prototype: data Maybe a = Just a | Nothing deriving (Eq, Ord)
-- Ex: Using Maybe for division
import Data.Maybe
safeDivide :: Int -> Int -> Maybe Int
safeDivide n 0 = Nothing
safeDivide n m = Just (n `div` m)
-- Run
safeDivide 12 3
--Out:
Just 4
safeDivide 12 0
--Out:
Nothing
Abstract Data Types
Here are some abstract data types/structures that I implemented for fun
Linked List:
A Linked List is relatively easy to implement. The linked list is made up of nodes. Each node has a value and a LList, which is just the next node in the list, and the final node has LList Null
data LList = Null | Node Int LList
instance Show LList where
show Null = "| . |"
show (Node a llist) = "| "++(show a)++" |---->"++show(llist)
addToList :: LList -> Int -> LList
addToList Null a = (Node a (Null))
addToList (Node a llist) b = (Node a (addToList llist b))
sumOfList :: LList -> Int
sumOfList Null = 0
sumOfList (Node a llist) = a+(sumOfList llist)
arrayToLList :: [Int] -> LList
arrayToLList [] = Null
arrayToLList (x:xs) = (Node x (arrayToLList xs))
removeAtK :: LList -> Int -> LList
removeAtK Null a = Null
removeAtK (Node a llist) 0=llist
removeAtK (Node a llist) b=(Node a (removeAtK llist (b-1)))
addAtK :: LList -> Int -> Int -> LList
addAtK Null i a = (Node a (Null))
addAtK (Node a llist) 0 b= (Node b (Node a (llist)))
addAtK (Node a llist) i b= (Node a (addAtK llist (i-1) b))
Example: Running the Linked List program:
-- Run it:
-- Create a Linked List:
a = (Node 2 (Node 4 (Node 5 (Node 1 (Null)))))
| 2 |---->| 4 |---->| 5 |---->| 1 |---->| . |
-- Add to List:
(addAtK a 3 9)
| 2 |---->| 4 |---->| 5 |---->| 9 |---->| 1 |---->| . |
-- Remove from List:
(addAtK a 2)
| 2 |---->| 4 |---->| 1 |---->| . |
-- Convert an Array to a Linked List:
(arrayToLList [1,2,3,4])
| 1 |---->| 2 |---->| 3 |---->| 4 |---->| . |
-- Get the sum of the Linked List:
(sumOfList a)
12
Queue
For a queue we define the back and front of the queue, which allows us to push and pop.
data MyQueue = Back Int MyQueue | Front Int | Node Int MyQueue
instance Show MyQueue where
show (Front curr) = " "++(show curr)++" "
show (Back curr next) = "| "++(show curr)++" | "++(show next)
show (Node curr next) = (show curr)++" |"++(show next)
insertElem :: MyQueue -> Int -> MyQueue
insertElem (Back curr next) n = (Back n (Node curr (next)))
deleteElem :: MyQueue -> MyQueue
deleteElem (Back curr next) = (Back curr (deleteElem next))
deleteElem (Node curr (Front n)) = (Front curr)
deleteElem (Node curr next) = (Node curr (deleteElem next))
Example: Running the Queue program:
-- Run it:
--Create a queue
a = (Back 2 (Node 3 (Node 1 (Front 8))))
| 2 | 3 |1 | 8
--Insert (Push) an element
insertElem a 5
| 5 | 2 |3 |1 | 8
--Delete (Pop) an element
deleteElem a
| 2 | 3 | 1
Arithmetic Tree:
Define a binary search tree where each leaf has a float, and each internal node has an operator
-- For School Assignment
-- Type Literal x
x :: Char
x = 'x'
-- Operators
data Op= Add | Sub | Mul | Div
--Show the Operators
instance Show Op where
show Add= " + "
show Sub= " - "
show Mul= " * "
show Div= " / "
-- Helper Function to apply the operators
applyOper :: Op -> Float -> Float -> Float
applyOper Add ls rs = ls + rs
applyOper Sub ls rs = ls - rs
applyOper Mul ls rs = ls * rs
applyOper Div ls rs = ls / rs
-- Recursive Data Structure for the Arithmetic Tree
data Expr = Lit Float | Var Char | Oper Op Expr Expr
---------------------------------
instance Show Expr where
show (Lit a) = " "++(show a)++" "
show (Var a) = " "++[a]++" "
show (Oper op ls rs) = "("++(show ls)++(show op)++(show rs)++")"
-- Solve the expression given the value of the literal x
solveExpr :: Expr -> Float -> Maybe Float
solveExpr (Var a) n = Just n
solveExpr (Lit a) n = Just a
solveExpr (Oper Div ls rs) n = (safeDiv a b) where
Just a = (solveExpr ls n)
Just b = (solveExpr rs n)
solveExpr (Oper op ls rs) n = Just (applyOper op a b) where
Just a = (solveExpr ls n)
Just b = (solveExpr rs n)
-- Perform a division such that if divided by 0 it will not return an error
safeDiv :: Float -> Float -> Maybe Float
safeDiv n 0 = Nothing
safeDiv n m = Just (n/m)
--------------------------
-- Draw Tree
-- Purpose: Function to draw tree
drawTree :: Expr -> [[Char]]
drawTree (Lit a)=[" "++(show a)++" "]
drawTree (Var a)=[" "++[a]++" "]
drawTree tree = (drawLevels tree (getLevels tree))
-- Purpose: takes the tree and max number of levels
-- recursively draws the left hand side of the tree and then the right side
-- IN:
-- - Expr - an Expression Tree
-- - Int - the number of layers in the tree
-- OUT:
-- - [[Char]] - the string representation of the subtree
drawLevels :: Expr -> Int -> [[Char]]
drawLevels (Lit a) n = [" ---- "++(show a)]
drawLevels (Var a) n= [" ---- "++[a]++" "]
drawLevels (Oper op ls rs) n= ["(" ++ (show op) ++ ")"++(drawLeft ls)] ++ (drawRight ls n) ++ (drawLevels rs (n-1))
-- Purpose: draws the right side of the tree
-- draws the vertical lines, as well as the right leaves as they must be on the same line in order for the tree to be connected
-- IN:
-- - Expr - an Expression Tree
-- - Int - the number of layers (vertical lines to draw)
-- OUT:
-- - [[Char]] - the string representation of the subtree
drawRight :: Expr -> Int -> [[Char]]
drawRight (Lit a) n =[" |"]
drawRight (Var a) n =[" |"]
drawRight (Oper op ls (Var a)) n=[(dupl (n-1) " | "),(dupl(n-2) " | ")++" ---- "++[a]]++(drawRight ls (n-1))
drawRight (Oper op ls (Lit a)) n=[(dupl (n-1) " | "),(dupl (n-2) " | ")++" ---- "++(show a)]++(drawRight ls (n-1))
drawRight (Oper op ls rs) n =[" |"]++(drawRight ls n)++(drawRight rs n)
-- Purpose: draws the "left hand side" of the tree
drawLeft :: Expr -> [Char]
drawLeft (Lit a)=" ---- "++(show a)
drawLeft (Var a)=" ---- "++[a]
drawLeft (Oper op ls rs)=" ---- ( " ++ (show op) ++ " )"++(drawLeft ls)
-- Purpose: duplicates a string a given amount of times
dupl :: Int -> [Char] -> [Char]
dupl 0 a=""
dupl n a=a++(dupl (n-1) a)
-- Purpose: gets the max number of layers in the tree or subtree, used for proper spacing when drawing the tree
getLevels:: Expr -> Int
getLevels (Lit a)=1
getLevels (Var a)=1
getLevels (Oper op ls rs)=if (getLevels ls) >= (getLevels rs) then 1+(getLevels ls) else 1 + (getLevels rs)
Example: Running the Arithmetic Tree Program:
-- Run it:
-- Create Tree
a = (Oper Add (Oper Sub (Lit 5) (Var x)) (Lit 2))
(( 5.0 - x ) + 2.0 )
-- Solve the Tree given x
solveExpr a 3
Just 4.0
-- Draw Tree
putStr (unlines (drawTree a))
( + ) ---- ( - ) ---- 5.0
| |
| ---- x
|
---- 2.0
Graphs:
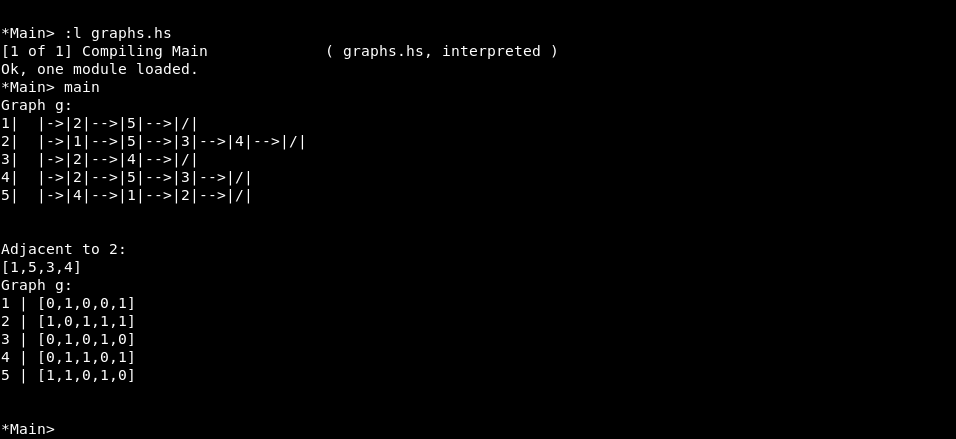
This was difficult as generally data types must be recursive. All the other ones implemented are acyclic, so they are easy, but graphs have cycles, so they are harder. An adjancency list-like and adajcency-matrix-like structures were used.
data AdjacencyList = Null | Node Int AdjacencyList
instance Show AdjacencyList where
show Null = "|/|"
show (Node a adjlist) = "|" ++ (show a) ++ "|-->" ++ (show adjlist)
data GraphList = NodeList Int AdjacencyList GraphList | None
instance Show GraphList where
show None = "\n"
show (NodeList x al gr) = (show x) ++ "| |->"++ (show al) ++ "\n" ++ (show gr)
adjacentListToList :: AdjacencyList -> [Int]
adjacentListToList Null = []
adjacentListToList (Node x adjlist) = x : (adjacentListToList adjlist)
getAdjacentVertices :: GraphList -> Int -> [Int]
getAdjacentVertices None v = []
getAdjacentVertices (NodeList x al gr) v = if x == v then (adjacentListToList al) else (getAdjacentVertices gr v)
data GraphMatrix = GNode Int [Int] GraphMatrix | MNull
instance Show GraphMatrix where
show MNull = "\n"
show (GNode v l gr) = (show v) ++ " | " ++ (show l) ++ "\n" ++ (show gr)
main = do
let g = (NodeList 1 (Node 2 (Node 5 Null)) (NodeList 2 (Node 1 (Node 5 (Node 3 (Node 4 Null)))) (NodeList 3 (Node 2 (Node 4 Null)) (NodeList 4 (Node 2 (Node 5 (Node 3 Null))) (NodeList 5 (Node 4 (Node 1 (Node 2 Null))) None)))))
putStrLn $ "Graph g: \n" ++ (show g)
putStrLn $ "Adjacent to 2:\n" ++ (show (getAdjacentVertices g 2))
let gr = (GNode 1 [0, 1, 0, 0, 1] (GNode 2 [1, 0, 1, 1, 1] (GNode 3 [0, 1, 0, 1, 0] (GNode 4 [0, 1, 1, 0, 1] (GNode 5 [1, 1, 0, 1, 0] MNull)))))
putStrLn $ "Graph g: \n" ++ (show gr)
Using the following as an example:
Result:
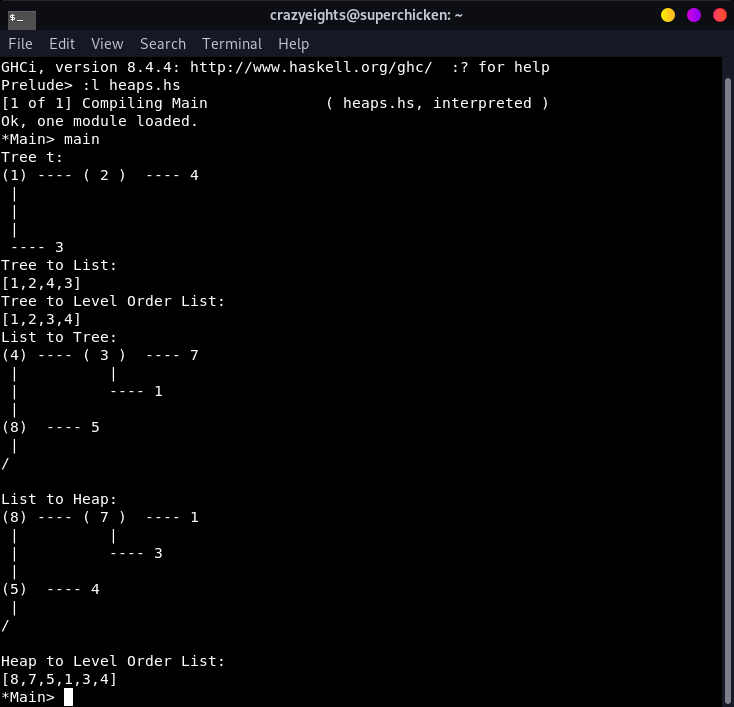
Heaps:
Heaps can be represented as lists, or as trees. This program converts between them several different ways. Note: it is missing several fundamental operations.
data BinTree = Node Int BinTree BinTree | Null
instance Show BinTree where
show Null = ""
show tree = (unlines (drawLevels tree (getLevels tree)))
drawLevels :: BinTree -> Int -> [[Char]]
drawLevels Null n= ["/"]
drawLevels (Node x Null Null) n = [" ---- "++(show x)]
drawLevels (Node x ls rs) n = ["(" ++ (show x) ++ ")"++(drawLeft ls)] ++ (drawRight ls n) ++ (drawLevels rs (n-1))
drawRight :: BinTree -> Int -> [[Char]]
drawRight (Node x Null Null) n =[" |"]
drawRight Null n= [" |"]
drawRight (Node r ls (Node x Null Null)) n=[(dupl (n-1) " | "),(dupl (n-2) " | ")++" ---- "++(show x)]++(drawRight ls (n-1))
drawRight (Node r ls rs) n =[" |"]++(drawRight ls n)++(drawRight rs n)
-- Purpose: draws the "left hand side" of the tree
drawLeft :: BinTree -> [Char]
drawLeft Null = "/"
drawLeft (Node x Null Null) =" ---- "++(show x)
drawLeft (Node x ls rs)=" ---- ( " ++ (show x) ++ " )"++(drawLeft ls)
-- Purpose: duplicates a string a given amount of times
dupl :: Int -> [Char] -> [Char]
dupl 0 a=""
dupl n a=a++(dupl (n-1) a)
treeToList :: BinTree -> [Int]
treeToList Null = []
treeToList (Node r ls rs) = r : (treeToList ls) ++ (treeToList rs)
levelOrderToList' :: BinTree -> Int -> [Int]
levelOrderToList' Null n = []
levelOrderToList' (Node r ls rs) 0 = [r]
levelOrderToList' (Node r ls rs) n = (levelOrderToList' ls (n-1)) ++ (levelOrderToList' rs (n-1))
getLevels :: BinTree -> Int
getLevels Null = 0
getLevels (Node r ls rs) = if (ln > rn) then ln+1 else rn+1 where
ln=(getLevels ls)
rn=(getLevels rs)
walkLevels :: BinTree -> Int -> Int -> [Int]
walkLevels t m 0 = []
walkLevels t n m = (levelOrderToList' t n) ++ (walkLevels t (n+1) (m-1))
levelOrderToList :: BinTree -> [Int]
levelOrderToList t = (walkLevels t 0 (getLevels t))
listToTree :: [Int] -> BinTree
listToTree [] = Null
listToTree (x:[]) = Node x Null Null
listToTree (x:xs) = (Node x (listToTree (take n xs)) (listToTree (drop n xs))) where n = (if mod (length xs) 2 == 1 then (div ((length xs)+1) 2) else (div (length xs) 2))
rebuildTree :: BinTree -> BinTree
rebuildTree Null = Null
rebuildTree (Node r Null Null) = (Node r Null Null)
rebuildTree (Node r (Node ls lls lrs) Null) | r > ls = (Node r (rebuildTree (Node ls lls lrs)) Null)
| otherwise = (Node ls (Node r lls lrs) Null)
rebuildTree (Node r Null (Node rs rls rrs)) | r > rs = (Node r (rebuildTree (Node rs rls rrs)) Null)
| otherwise = (Node rs (Node r rls rrs) Null)
rebuildTree (Node r (Node ls lls lrs) (Node rs rls rrs)) | r > ls && r > rs = (Node r (rebuildTree (Node ls lrs lls)) (rebuildTree (Node rs rls rrs)))
| r < ls && ls > rs = (Node ls (Node r lls lrs) (Node rs rls rrs))
| otherwise = (Node rs (Node ls lls lrs) (Node r rls rrs))
buildHeap' :: BinTree -> Int
buildHeap' Null = 0
buildHeap' (Node r Null Null) = 0
buildHeap' (Node r Null (Node rs rls rrs)) | r > rs = (buildHeap' (Node rs rls rrs))
| otherwise = 1
buildHeap' (Node r (Node ls lls lrs) Null) | r > ls = (buildHeap' (Node ls lls lrs))
| otherwise = 1
buildHeap' (Node r (Node ls lls lrs) (Node rs rls rrs)) | r > ls && r > rs = (buildHeap' (Node ls lls lrs)) + (buildHeap' (Node rs rls rrs))
| otherwise = 1
buildHeap :: BinTree -> BinTree
buildHeap tr = if (buildHeap' tr) == 0 then tr else (buildHeap (rebuildTree tr))
main = do
let t = (Node 1 (Node 2 (Node 4 Null Null) Null) (Node 3 Null Null))
putStr $ "Tree t: \n"++(show t)
putStrLn $ "Tree to List: \n"++(show (treeToList t))
putStrLn $ "Tree to Level Order List: \n"++(show (levelOrderToList t))
let arr = [4,3,7,1,8,5]
let tr = (listToTree arr)
putStrLn $ "List to Tree: \n" ++ (show tr)
let heap = (buildHeap tr)
putStrLn $ "List to Heap: \n" ++ (show heap)
putStrLn $ "Heap to Level Order List: \n"++(show (levelOrderToList heap))
Example Usage:
Create a tree and convert to list. Convert a list to tree, and convert list to max heap